Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
[ad_1]
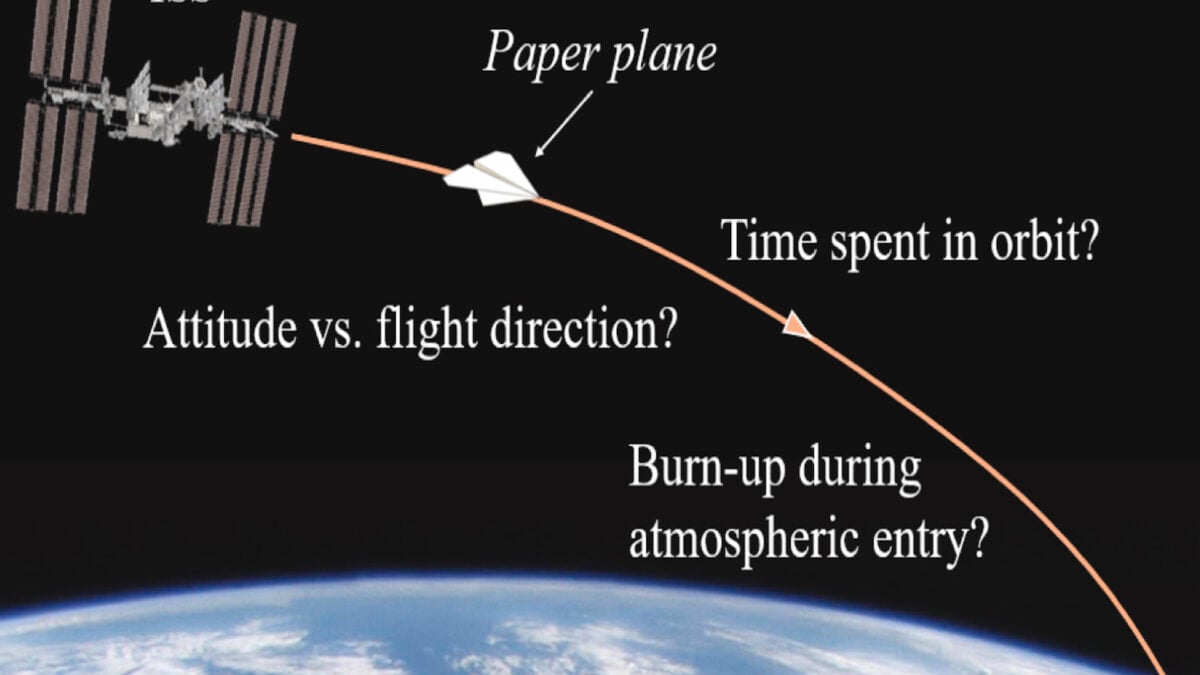
One day to build a spacecraft can be as simple as a piece of paper as a piece of paper wrapping into a plane and make aerodynamics. Tokyo Researchers’ team simulated the release of a paper plane from the International Space Station to see that the atmospheric reentry will survive.
To a paper published Researchers in ACTA Astronautica demonstrated how Origami could be a solution to the low ground orbit. The team behind the paper is that only a standard paper sheet behind the paper is that it can fulfill the work behind the paper and re-burned and easily burned in the atmosphere. For researchers, researchers have created a paper aircraft with an aluminum tail and placed it in the wind tunnel to see how to go in space. The idea is simple and aims to show how to use organic materials to create a more durable orbital environment.
Origami spacecraft A4 printing paper, coated A4 printing paper, is made of folded layers on the nose and provides aerodynamic stability. “Such a spacecraft has not yet flew in space.” “Their flight dynamics are not known whether in the high rarely atmosphere [low Earth orbit] It will look like an ordinary land-based origami origami plane and the plane survived or burned during the atmospheric entry. “Of course, the whole spacecraft will not be prepared only on paper. Instead, it can be built of a wing or drif sailing materials such as special components.
To try this, researchers first established the simulation of a paper aircraft with a height of 248 miles (400 kilometers), at a height of 248 miles (7,800 meters per hour). The paper plane remained stable and slipped into conditions like space. The earth’s surface (120 kilometers) began to fall from a height of 74 miles above 74 miles. Tumbling movement is expected in this height and the severe aerodynamic heat will result in the burning paper aircraft in the atmosphere at a height of about 55 to 58 miles (90 to 110 kilometers).
Researchers then placed a physical model in the University of Tokyo at the University of Tokyo and High Enthalpy in a hypersonic and high enthalpy wind tunnel. In about seven seconds, he exposed him to 7 speeds, and during which time the aircraft’s nose was bent and the wings showed signs. Although it was not fully divided, but it would be most likely to keep there for a long time, and researchers said.
With the atmospheric reentri, let the traditional spacecraft damaging the ozone layer of metal particles and chemicals. On the other hand, the paper plane is made of organic material that does not pose an environmental threat. There are still some of the remaining challenges. Given how small the paper aircraft is not reflected in radar enough and it will be difficult to follow in orbit. Researchers offer it to equip it with a miniature position, navigation and time transitions. It is also extremely sensitive to aerodynamic drag and therefore can only spend so much time in orbit, so it can be used for short-term missions with small loading.
Origami space plane will most likely not be a good fit for extensive missions, but can be used as a passive probe to lower a version of researchers or low and short-lived missions on the lower ground. “The extremely low price of a paper spacecraft can also be repeated at the same time with numerous placement, which provides distributed measurements at the same time and repeated in regular intervals.
The idea of the space plane as a sliding child can look very simple, but to use paper on the spacecraft, the metal blocking can help resolve the overpopulation of low ground orbit.
[ad_2]
Source link